1.雌成虫を識別する(識別の準備)
識別の準備1
識別の準備2
In this section, we show an easy way for beginners to discriminate Japanese species. In this way, we focus on 15 species collected frequently in the past in Japan and on 9 species of morphological similarity.
In advance, prepare the slide specimens of adult females, and check whether each specimen is an adult female or not as below. Then, go to STEP 2
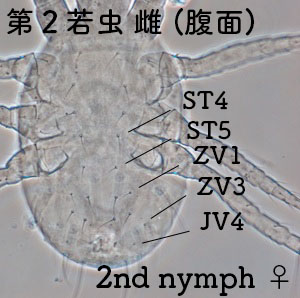
1. Count the dorsal setae. The specimen maybe a Japanese phytoseiid species if less than 22 pairs.
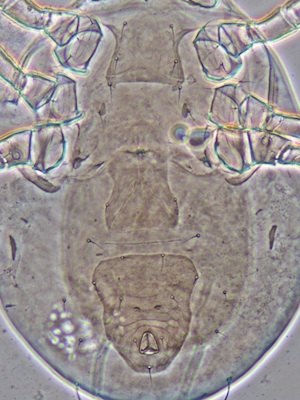
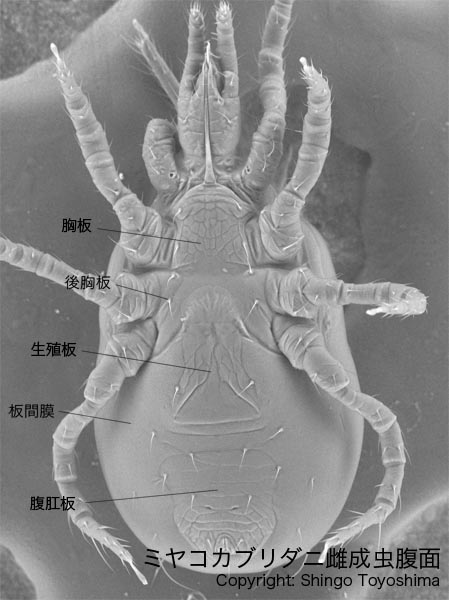
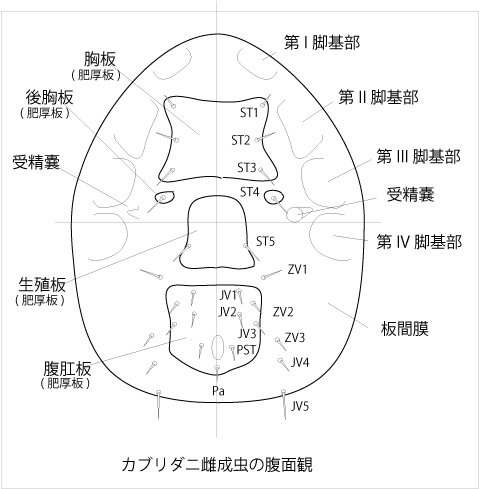
2. Check the shields (plates) on the ventral surface. The specimen maybe an adult female of a phytoseiid species if it has sternal, genital, and ventri-anal shields.
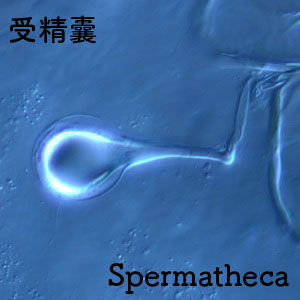
3. Check the spermathecae around the coxa of III and IV legs. The specimen must be an adult female if a spermatheca is observed at least at one side.
Inadequate specimens
4. The specimen may not be a phytoseiid species if it has 22 pairs or more.
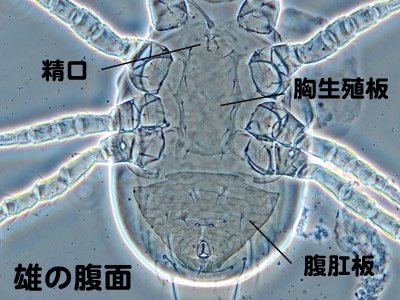
5. The specimen maybe an adult male if it has sterno-genital and ventri-anal shields. The male specimen has a spermatodactyl on both chelicerae.
An exception
The ventri-anal shield is not clearly observed on the ventral surface of a species, Gynaeseius liturivorus.
Go to STEP 2 if the specimen is an adult female of phytoseiid species.